Avoid the large strides through global memory, 尽可能 Global Memory Coalescing 全局内存合并
将 threads 分组为 warps 不仅与计算相关,还与全局内存访问相关。device 将 warp 内 threads 发出的全局内存 load/store 合并到尽可能少的事务(transactions)中,以最大限度地减少 DRAM 带宽。
Arrays allocated in device memory are aligned to 256-byte memory segments by the CUDA driver.
数组的起始地址对齐到 256 字节,这种对齐方式有助于提高内存访问效率。设备可以通过与其大小对齐的 32、64 或 128 字节事务来访问全局内存。
template <typename T>
__global__ void offset(T *a, int s)
{
int i = blockDim.x * blockIdx.x + threadIdx.x + s;
a[i] = a[i] + 1;
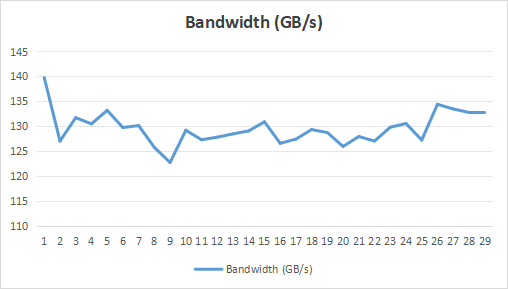
}通过设置一些 offset 来测试未对齐情况下,kernel 的带宽性能,如下图。可以看到会有一些影响,但影响不是非常严重。SM 上都会有 L1 cache,同时 warp 内 threads 的访问合并到尽可能少的 cache lines 中,从而导致是否对齐对数据访问的影响不至于很大。
Misaligned Data Accesses
template <typename T>
__global__ void stride(T *a, int s)
{
int i = (blockDim.x * blockIdx.x + threadIdx.x) * s;
a[i] = a[i] + 1;
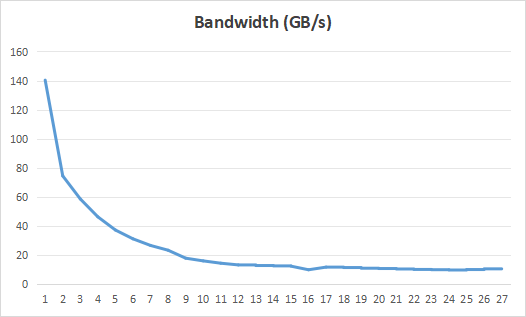
}但对于跨步全局内存访问,存在着不同的情况。特别是对于 large strides, 任何架构的有效带宽都会很差。原因显而易见:当并发线程同时访问物理内存中相距很远的内存地址时,硬件没有机会组合这些访问,每次访问的有效数据占比很低。
Strided Memory Access
而在访问多维数组时,线程通常需要索引数组的较高维度,因此跨步访问不可避免。这时,可以使用 shared memory 来处理这种情况。shared memory 是线程块中所有线程共享的片内内存。
共享内存的一种用途是以合并的方式从全局内存中加载多维数组的 2D tile 块到共享内存中,然后让连续的线程跨步访问共享内存 tile,不像 global memory,shared memory 的跨步访问开销很小。
总结
GPU global memory 访问与 host 端数据访问类似,数据局部性非常重要。在早期 CUDA 硬件上,内存访问对齐与线程间的局部性一样重要,但在最新的硬件上跨步内存访问更加重要,需要使用一些优化方法来缓解,如 shared memory。
最后
GPT4 给出的答案:
Accessing global memory efficiently in CUDA kernels involves several strategies:
- Coalesced Accesses:
- Ensure that threads in a warp access consecutive memory addresses. This allows the memory controller to combine these accesses into fewer transactions.
- Memory Alignment:
- Align data structures to 32, 64, or 128 bytes. Proper alignment reduces the number of memory transactions needed.
- Use Shared Memory:
- Load data from global memory into shared memory when possible. Shared memory is much faster and can be used to reduce redundant global memory accesses.
- Minimize Divergence:
- Avoid branching and ensure threads in a warp follow the same execution path to maximize memory throughput.
- Optimize Memory Patterns:
- Use structure-of-arrays (SoA) instead of array-of-structures (AoS) to allow coalesced accesses.
- Use Read-Only Cache:
- For read-only data, use the
__ldg()intrinsic to leverage the read-only data cache, which can improve access speed.
- For read-only data, use the
- Avoid Bank Conflicts:
- When using shared memory, ensure that memory accesses do not lead to bank conflicts, which can slow down access.
这里相当于介绍了第 1 点和第 2 点,提了一嘴第 3 点,后面有机会再总结。
参考:How to Access Global Memory Efficiently in CUDA C/C++ Kernels | NVIDIA Technical Blog
代码: code-samples/series/cuda-cpp/coalescing-global/coalescing.cu (github.com)