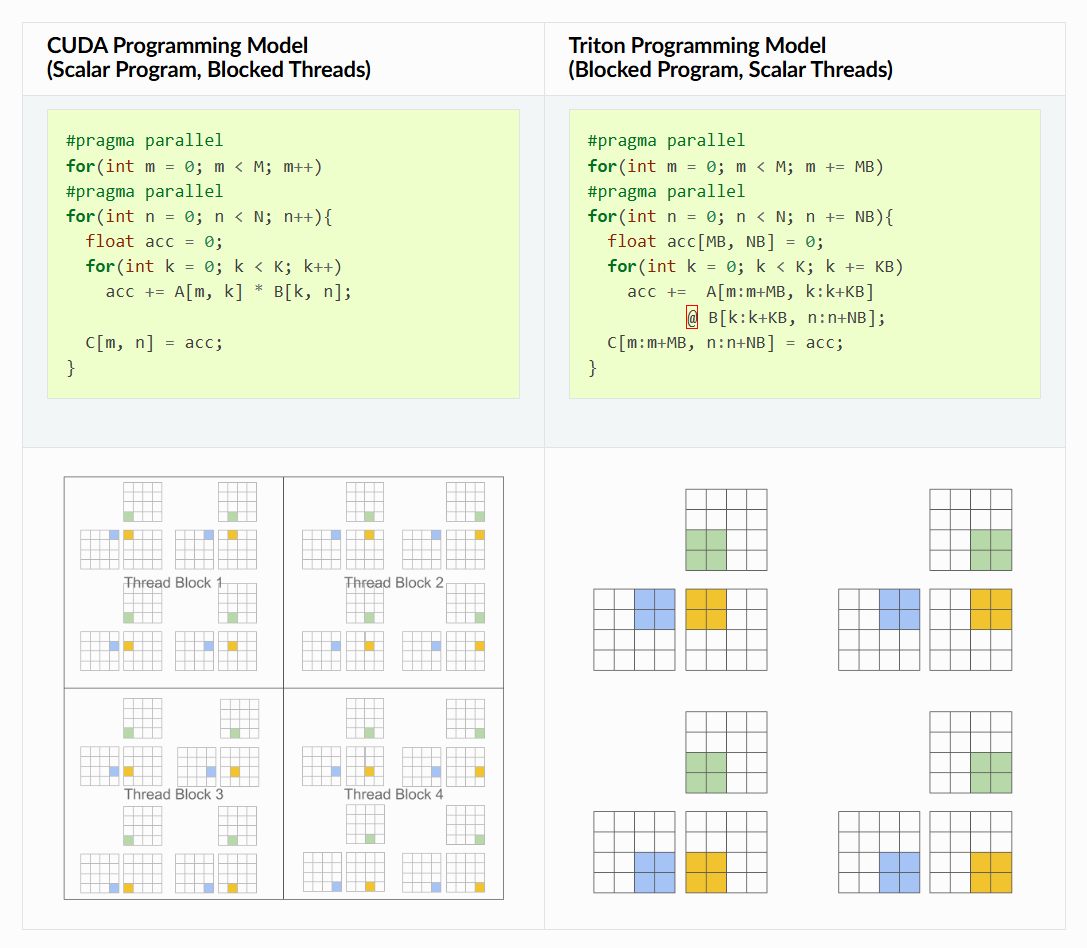
Triton 编程模型与 CUDA 编程模型
Scalar Program,Blocked Threads 和 Blocked Program,Scalar Threads 编程模型区别:
上图左侧是 CUDA kernel,右侧是 Triton kernel。同样是计算矩阵 C 中的 4 个元素,左下图使用一个 Thread Block1 (包含 4 个线程) 来实现,对应的 kernel 代码是线程粒度,每个线程处理矩阵 C 中的 1 个元素。
而右侧是 Triton kernel,是线程块粒度,直接处理矩阵 C 中的 4 个元素。区别在这里,同样是处理矩阵 C 中的 4 个元素,一个 CUDA kernel 表示一个线程运行的逻辑代码,处理一个元素。一个 Triton kernel 直接处理 C 中的 4 个元素,表示线程块运行的逻辑代码,处理一批元素。
Triton kernel 主要好处在于,会产生 block 结构的并行迭代空间,在实现稀疏运算时,为程序员提供比现有 DSL 更大的灵活性,同时允许编译器编译时优化 kernel 程序的 data locality 和 parallelism.
Note
The main challenge posed by our proposed paradigm is that of work scheduling, i.e., how the work done by each program instance should be partitioned for efficient execution on modern GPUs.
结合下面这个人话及例子更好理解:
With CUDA, we decompose the computation in 2 levels: First into blocks, then each block further into threads. All threads in a block run on the same SM and share the same Shared Memory. And each thread computes on scalars.
In Triton, we decompose the computation only in 1 level: Into blocks. There is no further decomposition into threads. Triton requires us to perform operations on vectors. Also, we don't need to and are not able to manage the shared memory. Triton does that automatically.
All operations in triton kernels are vectorized: Loading data, operating on data, storing data, and creating masks.
在 Triton 编程语义中,每个 kernel (处理一个 block)被称为一个 program,实际上 pid 就是 program id,也即是 block id(等同于 CUDA kernel 中 block id 的概念)。但 Triton 编程模型决定了,block 下面没有更细的 thread 了,所以写 triton kernel 时,要考虑处理的是一个 block 数据块。
lectures/lecture_014/A_Practitioners_Guide_to_Triton.ipynb at main · gpu-mode/lectures
强烈推荐看一下上面链接中关于 Triton 编程模型的介绍和举例,理解起来比官网文档要顺畅很多。